The Benefits of Split Spherical Roller Bearings

First published in the July 2020 issue of Quarry Management as Conveying with Confidence
When it was first introduced a little over a century ago, the heavy-duty belt conveyor revolutionized the mining, quarrying and cement industries. Maintaining this machinery, however, continues to be a slow, expensive and dangerous task. Clive Jennings, product manager for SKF Cooper split bearings at SKF, proposes a solution to these problems
Despite significant reductions, the number of injuries and fatalities that occur in the mining industry each year remains high. Many of the incidents happen when maintenance and repairs are being carried out, and industry studies have found that 43% of all accidents and 24% of all fatalities occur during maintenance work on conveyors. This is partly because couplings and gearboxes on this type of equipment need to be hoisted during repair, which creates a number of risks to the safety of employees.
In the mining, quarrying and cement industries, conveyors are by far the most troublesome machinery to keep running efficiently. One problem is grease consumption; conveyors typically use standard open-pulley bearings, which require large amounts of grease to purge any contamination. Furthermore, open bearings have a relatively short service life and, therefore, normally do not last as long as the pulley lagging itself.
The premature failure of bearings entails their frequent repair and replacement. To compound the issue, this is time-consuming, costly and, as mentioned, poses inherent risks that could lead to serious injuries or fatalities. Since bearings are often situated in difficult to access locations, it can take up to 24h to replace them.
Preventing the contamination of conveyor bearings, reducing the amount of lubrication they need and speeding up repair times are, therefore, crucial challenges for the mining, quarrying and cement industries. In response to these challenges, SKF Cooper split spherical roller bearings are designed to counteract the contamination that so frequently causes open pulley bearings to fail, to extend the service life of the bearing and to significantly reduce downtime, maintenance costs and risks to workers by the replacement of bearings in situ. A sealed variant is also available that greatly reduces the need for lubrication by providing effective protection against contamination.
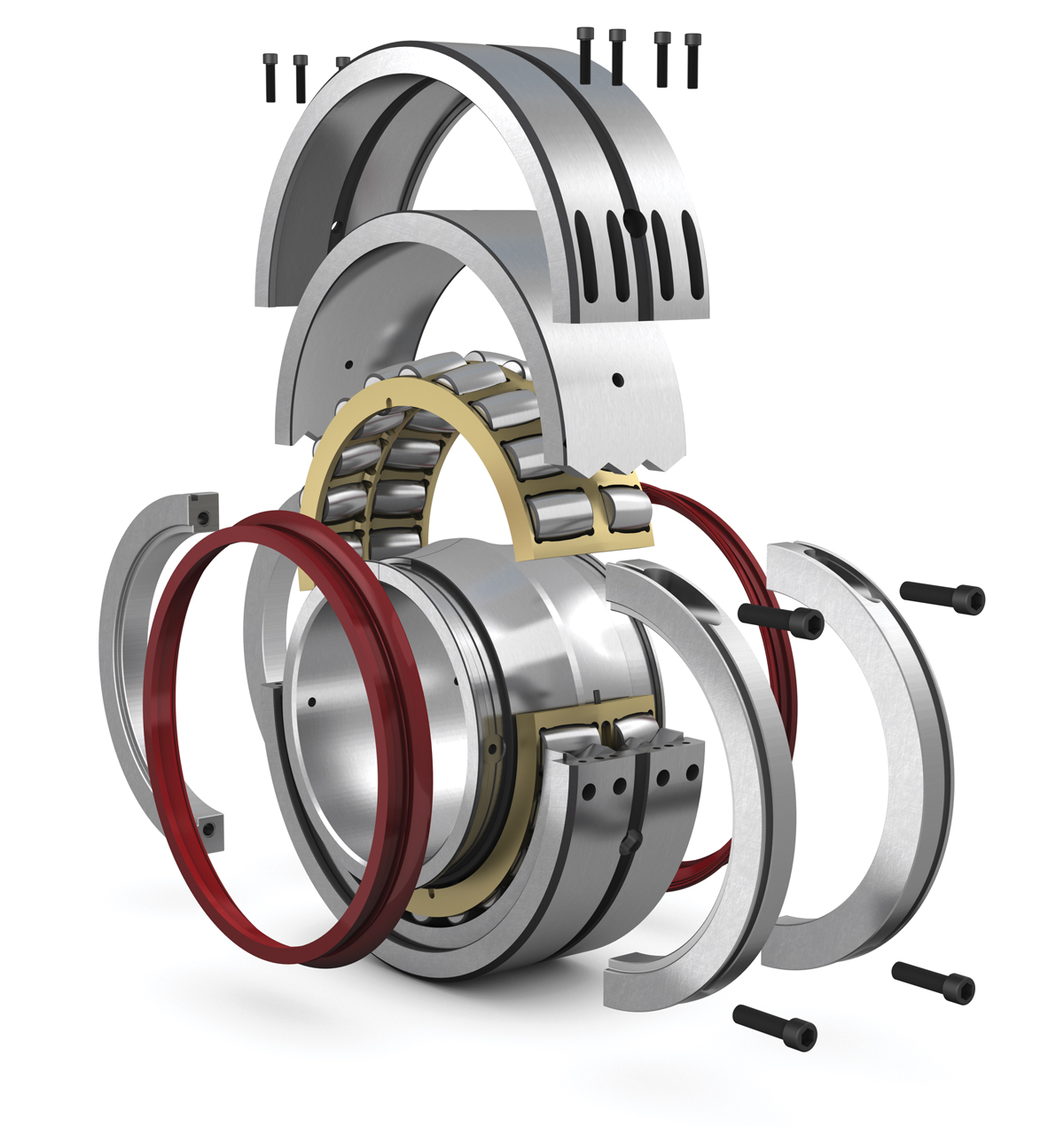
The bearing comprises inner/outer rings, a cage and rollers, an outer shroud, two inner clamp rings, and screws to bolt the shrouds and clamp the rings together. The design of the rings, in particular, serves to enhance the performance of the bearing and increase its service life. Both the inner and outer rings are wire cut to minimize discontinuities, ensuring superior clamping and the accurate alignment of the two halves of the ring. The interlocking outer race and shroud joints not only provide good alignment of the two halves, but also reduce the risk of damage at the splits during operation. The wire cut angular inner race joints further ensure a smooth roller path.
Moreover, using wire cutting as a splitting technique – rather than employing alternative methods – means that the risk for fretting corrosion with the shaft is minimized. Finally, the steel clamp rings allow permissible axial loads (shaft clamping) some 50–100% greater than comparable split spherical roller bearings and they are even quieter during operation.
For customers looking for bearings designed to be easily replaced in situ, with minimal disturbance to the shaft alignment or driveline, the use of SKF Cooper split spherical roller bearings can reduce mean time to repair (MTTR) by as much as 70%.
The main use of the split spherical roller bearing is in the trapped bearing position of the machine. Here, the replacement of a bearing with a standard (non-split) version would require the removal (hoisting) of the gearbox and drive coupling. With the SKF Cooper split bearing, the number of actions required to replace a bearing in the trapped position is reduced from 17 to just eight (see panel).
For example, the use of a split bearing eliminates the need to make any changes to the alignment of the shaft or driveline. There is no need to dismount the drive coupling or cantilevered drive, thus reducing the amount of equipment, such as cranes and alignment tools, that need to be rented to complete the job.
Moving the conveyor belt to access the pulley, and moving the pulley and gearbox, can be very dangerous operations to carry out, as these components are often heavy and elevated above ground, thereby increasing the risk of an accident to maintenance personnel. By contrast, in-situ replacement of a split bearing only requires the slight raising of the shaft and little or no disturbance of the drive coupling or gearbox, which greatly reduces the exposure of workers to safety hazards.
As a further benefit, the use of a sealed split bearing significantly reduces the need for lubrication (approximately 90–95% less grease), resulting in reduced costs, safety risks and environmental impact.
The SKF Cooper range of split spherical roller bearings can be fitted in all SKF metric (SNL, SNLD) and inch (SAF, SAFD, SDAF) split plummer block housings. The split bearing outer ring has the same dimensions as a standard spherical roller bearing and can fit into split plummer block housings with standard locating rings, if required. The shaft requirements of the split bearing are the same as those needed for a standard spherical roller bearing mounted on an adapter sleeve.
Ultimately, the use of SKF Cooper split spherical roller bearings can help those in the mining, quarrying and cement industries to significantly cut their maintenance costs and production losses, and reduce their environmental impact – whilst improving worker safety.
Sequence of procedures for replacing a bearing in the trapped position
Standard bearing
- Safety lockout/tagout
- Block machine (pulley) from rotation
- Block and move belt to access pulley
- Disconnect gearbox coupling from motor
- Disconnect gearbox coupling from machine
- Remove coupling from machine
- Lift and remove gearbox
- Remove split block housing cap
- Lift and support machine shaft
- Remove and replace bearing
- Replace housing cap
- Reposition gearbox
- Connect gearbox to machine
- Connect gearbox to motor
- Check alignment of motor to gearbox
- Remove machine blocking
- Remove safety lockout/tagout.
Split bearing
- Safety lockout/tagout
- Block machine (pulley) from rotation
- Remove split block housing cap
- Lift and support machine shaft
- Remove and replace bearing
- Replace housing cap
- Remove machine blocking
- Remove safety lockout/tagout.
- Subscribe to Quarry Management, the monthly journal for the mineral products industry, to read articles before they appear on Agg-Net.com